Understanding Why Password Strength Matters Bitcoin wallets are secured by private keys and passwords that act as digital locks. If someone gains access to them, your funds could vanish in seconds. That’s why strong password habits are not just recommended—they’re a core part of protecting your assets. A common mistake is relying on passwords that […]
Choosing the Wrong Hardware for the Job Starting off with the wrong equipment can cost more than just money. Bitcoin mining requires specialized machines known as ASICs. These devices are built for one thing—solving complex equations that support the Bitcoin network. Trying to use a regular computer or outdated miner often leads to wasted electricity […]
Why a Recovery Phrase Deserves Serious Attention A recovery phrase is the master key to your bitcoin wallet. If lost, stolen, or exposed, it can mean permanent loss of access to your funds. Unlike traditional banking, there’s no customer support to call for password resets. The responsibility—and the risk—rests entirely with the holder. Because of […]
Understanding the Basics of Ordinals on Bitcoin Ordinals bring a new layer of meaning to Bitcoin by assigning unique identities to individual satoshis—the smallest unit of BTC. Through a method called “inscription,” each satoshi can now carry data, such as images, text, or code. This process has turned Bitcoin into more than just a currency; […]
Why understanding Bitcoin software options matters Bitcoin is more than just a digital currency. It’s a network powered by different types of software, each with its own purpose. One of the most talked-about is Bitcoin Core—a reference point in the ecosystem. But it’s not the only option available. Understanding how it compares to other software […]
Why ROI Calculators Matter for Bitcoin Investments Bitcoin remains one of the most dynamic and widely discussed investment assets, attracting both long-term investors and short-term traders. Given its high price fluctuations, measuring profitability is essential for anyone looking to navigate the crypto market successfully. One of the most effective ways to do this is by […]
Why mining nodes matter to everyone using Bitcoin Bitcoin works without a central authority, which makes it different from traditional payment systems. But without banks or admins, how does it stay secure? The answer lies in mining nodes—those silent machines running in the background that play a major role in keeping Bitcoin safe and reliable. […]
Understanding why mining rewards rise and fall Bitcoin mining isn’t just about powerful machines solving complex math problems. There’s a rhythm behind it that many overlook. Mining difficulty plays a key role in how much a miner earns, and it’s a setting that quietly shifts every two weeks. For those running rigs at home or […]
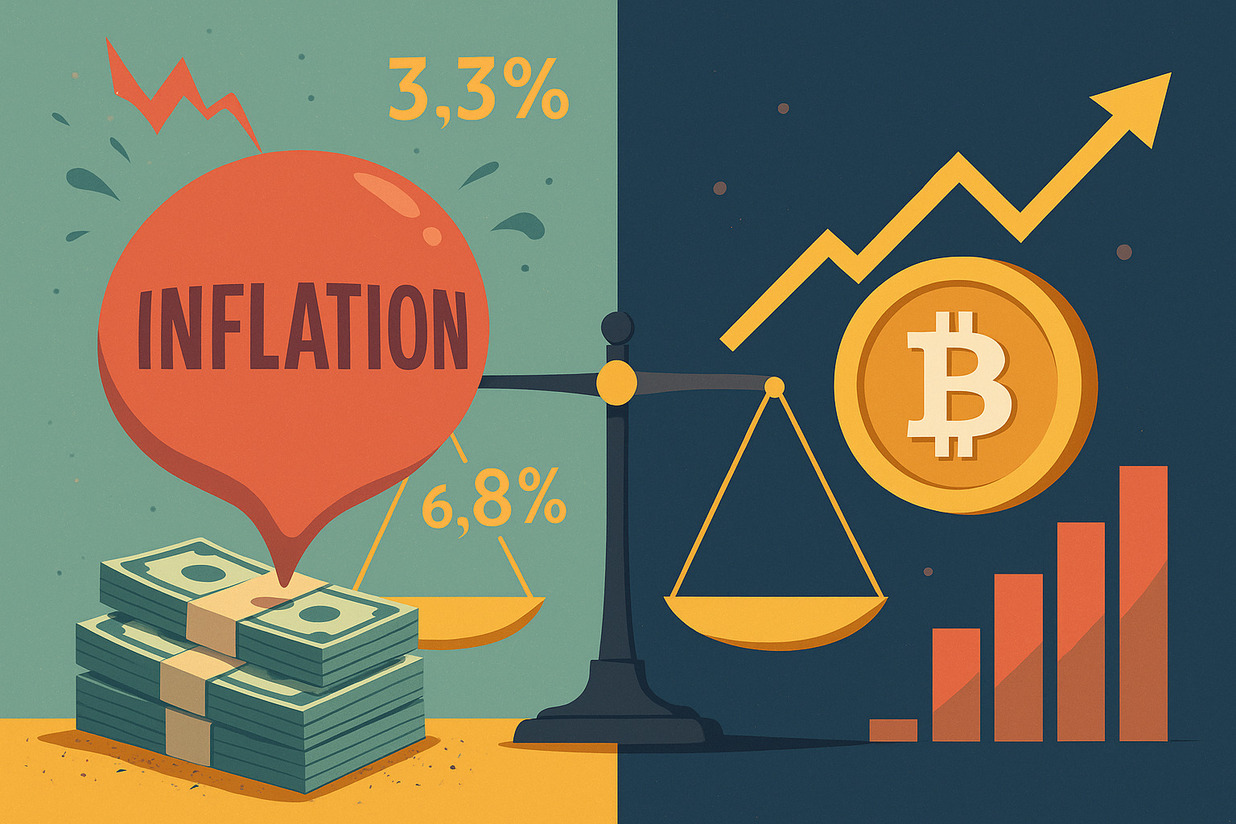
Understanding the Value of Bitcoin Amid Rising Prices As prices of goods continue to climb, many people are looking for ways to protect their money. It’s not just about saving—it’s about where to safely store the value of your hard-earned income. This leads to questions about Bitcoin—a digital asset often compared to gold when it […]
Why It’s Important to Learn How to Send and Receive Bitcoin As the number of cryptocurrency users—especially Bitcoin—grows, so does the need to know how to use it safely and correctly. For beginners, the idea of sending or receiving Bitcoin may sound technical. In reality, however, it’s simple and straightforward once you understand the proper […]