The Role of Miners in Operating the Bitcoin Network
Bitcoin is a digital currency that operates without the control of any bank or government. Instead, it relies on a network of computers to maintain security and process transactions. Miners play a crucial role in this system, as they verify each transaction before it is officially added to the blockchain.
Whenever a new transaction is initiated on the Bitcoin network, it must be approved before being recorded. Miners use powerful computers to ensure that every transaction is legitimate. Through cryptographic verification, they prevent fraudulent activities such as double-spending, where someone attempts to use the same Bitcoin more than once.
Beyond securing transactions, mining serves another vital function—introducing new Bitcoin into circulation. The rewards that miners receive incentivize their participation in the mining process, helping sustain the entire Bitcoin system and its decentralized financial model.
Processing Transactions Through Bitcoin Mining
Every Bitcoin transaction contains essential details, including the sender’s address, the recipient’s address, and the amount being transferred. Before a transaction is officially processed, it must pass through network nodes, which filter out invalid transactions.
Once a transaction is verified, it enters the mempool, a temporary storage for unprocessed transactions. Miners select which transactions to process, often prioritizing those with higher transaction fees, as these provide better incentives.
After selecting transactions, miners bundle them into a block and submit it for mining. At this stage, miners utilize computational power to solve a mathematical puzzle, a process that ensures the new block can be added securely to the blockchain.
Building a Bitcoin Block on the Blockchain
The blockchain is a continuous ledger of transactions, where each block contains data from previous transactions. Every new block strengthens the security of the Bitcoin network, making it increasingly difficult to alter or manipulate the recorded data.
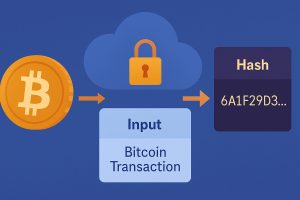
Each block includes a hash, a unique digital fingerprint representing its contents. This hash connects each block to the next, ensuring that any changes to one block would impact the entire chain. This structure makes it impossible to alter a transaction without the network detecting the modification.
Once a block is successfully added to the blockchain, all the transactions within it are considered officially confirmed. These transactions become immutable, meaning they cannot be reversed or modified. This trustless system eliminates the need for a central authority to validate transactions, reinforcing Bitcoin’s decentralized nature.
The Importance of Proof of Work in Bitcoin Security
Bitcoin uses the Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism to maintain the security of its network. Under this system, miners must solve a complex computational problem before they can add a new block to the blockchain.
This mechanism prevents attacks such as the 51% attack, where a single entity could potentially gain enough computational power to manipulate the blockchain. Since controlling the Bitcoin network requires enormous energy and resources, launching such an attack becomes impractical and financially unfeasible.
Apart from security, Proof of Work ensures fair distribution of Bitcoin. No single entity can dominate the network without making a significant computational contribution. Miners are rewarded with newly created Bitcoin, providing a natural incentive to continue mining and securing the system.
Mining Rewards for Each Block
When a miner successfully adds a block to the blockchain, they receive a block reward. This reward consists of newly minted Bitcoin along with transaction fees from the included transactions.
Bitcoin undergoes a process known as halving every four years, reducing the block reward by half. Initially, the reward was 50 BTC per block, but it has since decreased to 6.25 BTC. In the future, it will continue declining until no new Bitcoin is created, leaving miners dependent solely on transaction fees for earnings.
As block rewards diminish, Bitcoin mining becomes increasingly challenging and expensive. Miners must invest in advanced hardware to stay competitive, requiring significant computational power and energy efficiency to maximize profitability.
Selecting Transactions to Include in a Block
Not all transactions are processed immediately. Each transaction must pass through the mempool, where it waits until a miner selects it for inclusion in a block.
Miners generally prioritize transactions with higher fees. Due to competition among miners, they opt for transactions that offer better financial incentives, ensuring they maximize their earnings.
Transactions with lower fees may experience delays before being confirmed. During periods of high network congestion, it can take hours or even days for low-fee transactions to be processed, as miners favor those with higher rewards.
Impact of Mining Difficulty on Bitcoin Processing
Mining difficulty is an adjustable metric designed to regulate the pace at which new blocks are added to the Bitcoin blockchain. Every 2,016 blocks, or approximately every two weeks, the network recalibrates mining difficulty based on the total computational power being used.
When more miners participate, the difficulty increases to prevent blocks from being generated too quickly. Conversely, if miner participation decreases, the difficulty is lowered to ensure mining remains feasible.
This adjustment mechanism maintains Bitcoin’s security and prevents rapid inflation of new blocks. By balancing difficulty, the system ensures that blocks are consistently produced at an interval of approximately ten minutes, preserving Bitcoin’s foundational protocol.
Advancements in Bitcoin Mining Technology
Bitcoin mining technology has evolved significantly over time. In the early days, regular computers were sufficient for mining. However, as network difficulty increased, miners had to transition to more powerful hardware, such as ASIC miners, which are specialized devices designed specifically for Bitcoin mining.
Due to the high energy consumption associated with mining, many operations have shifted toward renewable energy sources to reduce costs. Countries with low electricity rates, such as Iceland and Kazakhstan, have become major hubs for large-scale Bitcoin mining farms.
Future developments in mining technology may introduce more energy-efficient solutions, improving profitability while reducing environmental impact. As the industry advances, companies continue investing in innovative methods to maintain competitiveness in Bitcoin mining.
The Future of Bitcoin Mining and Blockchain Security
The future of Bitcoin mining is constantly evolving in response to technological advancements and regulatory changes. As block rewards continue to decrease due to Bitcoin halving, transaction fees are expected to become the primary source of income for miners. Once Bitcoin reaches its maximum supply of 21 million coins, miners will no longer receive block rewards, relying solely on transaction fees for sustainability.
With mining becoming increasingly expensive, only the most efficient mining operations will thrive. Many miners are likely to shift toward large-scale, energy-efficient mining farms that leverage renewable energy sources. The adoption of more cost-effective solutions will play a crucial role in maintaining Bitcoin’s decentralized infrastructure.
Despite these challenges, mining remains the backbone of Bitcoin’s security. The Proof of Work mechanism ensures the network’s resilience against fraud and cyber threats. As long as miners continue dedicating their computational power to the network, Bitcoin will remain a secure and transparent digital currency. Ongoing advancements in mining hardware, alongside potential layer-2 solutions to optimize transaction processing, will further shape the future of the Bitcoin ecosystem. With continuous innovation and collaboration within the mining community, Bitcoin is poised to maintain its status as a reliable, decentralized financial system for years to come.















No Responses