Bitcoin: A Revolutionary Step in Digital Finance
Bitcoin represents a groundbreaking shift in the financial world and stands as the first truly decentralized digital currency. Satoshi Nakamoto, an anonymous individual or group, introduced it in 2009 to challenge traditional currencies controlled by central banks and governments. Instead of relying on a central authority, Bitcoin runs on a peer-to-peer network built on blockchain technology, which ensures secure, transparent, and efficient transactions.
Moreover, Bitcoin matters now more than ever because the global economy continues to move toward digital solutions. It tackles major issues in traditional financial systems, including high transaction fees, slow cross-border transfers, and limited access to banking services for underserved populations. Additionally, Bitcoin disrupts the conventional monetary system by offering a currency independent of any government or centralized entity.
Therefore, whether you are considering investing in Bitcoin, fascinated by the technology behind it, or analyzing its impact on the global economy, this guide provides essential insights into why this digital asset has become such a transformative force in modern finance.
The Purpose of Bitcoin
Bitcoin was born out of a desire to address the inefficiencies and vulnerabilities of traditional financial systems. To fully grasp its purpose, it’s essential to understand the context in which it was created.
Why Bitcoin Was Created: A Response to the Financial Crisis
The financial crisis of 2008 exposed the fragility of centralized banking systems, leading to widespread mistrust in financial institutions. Satoshi Nakamoto published the Bitcoin whitepaper in October 2008, proposing a decentralized digital currency that eliminates the need for intermediaries like banks. By removing centralized control, Bitcoin aimed to give individuals more power over their finances.
Peer-to-Peer Digital Cash
At its core, Bitcoin was designed to function as a peer-to-peer digital cash system. This means users can send and receive payments directly, without relying on a third party to process the transaction. Whether you’re transferring funds to a friend next door or a business partner halfway across the world, Bitcoin enables seamless and borderless payments.
Key Benefits of Bitcoin
Bitcoin offers numerous advantages that make it an attractive alternative to traditional currencies:
- Transparency: Every Bitcoin transaction is recorded on a public ledger called the blockchain, ensuring accountability and preventing fraud.
- Lower Transaction Fees: Bitcoin transactions typically involve minimal fees compared to conventional banking systems or money transfer services.
- Financial Inclusion: Bitcoin provides access to financial services for millions of people in developing regions who lack access to traditional banking infrastructure.
- Borderless Payments: With Bitcoin, geographical boundaries are irrelevant. You can send or receive funds anywhere in the world, as long as you have an internet connection.
Bitcoin’s decentralized nature and unique benefits have made it a powerful tool for individuals seeking greater control and freedom in managing their finances.
A Brief History of Bitcoin
Bitcoin’s journey from a niche concept to a global phenomenon is marked by milestones that showcase its resilience and innovation.
The Genesis Block and the Bitcoin Whitepaper
Bitcoin’s story begins with the publication of its whitepaper, titled “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System.” This document outlined how Bitcoin would function, introducing key concepts like blockchain, proof-of-work, and decentralization. On January 3, 2009, Satoshi Nakamoto mined the first block of the Bitcoin blockchain, known as the Genesis Block, embedding a message referencing the financial crisis as a critique of traditional banking.
Early Transactions and Adoption
In 2010, Bitcoin gained attention when Laszlo Hanyecz made the first known transaction, purchasing two pizzas for 10,000 BTC. This moment highlighted Bitcoin’s potential as a medium of exchange. Around this time, early adopters began mining Bitcoin and trading it on fledgling exchanges, laying the foundation for its community.
Milestones in Bitcoin’s Growth
Over the years, Bitcoin has achieved significant milestones:
- 2013: Bitcoin reached a $1 billion market capitalization, signaling growing interest from investors.
- 2017: Bitcoin’s price soared to nearly $20,000, driven by increasing adoption and media coverage.
- 2021: Major companies like Tesla and Square added Bitcoin to their balance sheets, and El Salvador became the first country to adopt Bitcoin as legal tender.
Today, Bitcoin is not only a digital currency but also a store of value and an asset class that has captured the attention of individuals, businesses, and governments worldwide.
How Bitcoin Works
Bitcoin’s operation is powered by groundbreaking technology that ensures security, transparency, and decentralization. Let’s break down its mechanics.
What Is Blockchain Technology?
At the heart of Bitcoin lies blockchain—a decentralized ledger that records every transaction on the network. Unlike traditional databases, blockchain operates across a network of computers (nodes), making it resistant to tampering and central control. Key features of blockchain include:
- Decentralization: No single entity controls the network, ensuring transparency and fairness.
- Immutability: Once data is added to the blockchain, it cannot be altered, preventing fraud.
- Transparency: All transactions are visible to the public, fostering trust among users.
Mining and Transaction Validation
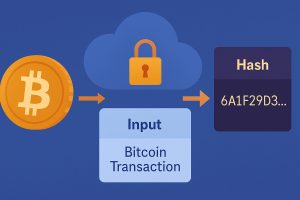
Bitcoin transactions are verified through a process called mining. Miners use powerful computers to solve complex mathematical problems, known as proof-of-work. Successful miners validate transactions and add them to the blockchain in blocks. As a reward, they receive newly created Bitcoin, incentivizing their participation and maintaining network security.
How Bitcoin Transactions Occur
Bitcoin transactions involve digital wallets, which generate unique public and private keys. The public key acts as the recipient’s address, while the private key is used to sign transactions securely. If you’re new to Bitcoin, setting up a Bitcoin wallet is the first step to sending and receiving transactions. Once initiated, the transaction is broadcast to the network, verified by miners, and confirmed on the blockchain.
Why Bitcoin Matters Today
As Bitcoin continues to evolve, its relevance in the global economy becomes increasingly evident.
Adoption Trends
Bitcoin’s adoption has grown significantly over the past decade. Individuals use it for payments, savings, and investment. Businesses, from small retailers to global corporations, accept Bitcoin as payment. Governments, too, are exploring its potential, with countries like El Salvador integrating Bitcoin into their financial systems.
Real-World Use Cases
Bitcoin’s versatility makes it valuable across various use cases:
- Remittances: Bitcoin offers a low-cost, fast alternative for sending money across borders, benefiting millions of migrant workers and their families.
- Investment: Many view Bitcoin as digital gold—a store of value that protects against inflation and economic uncertainty.
- Financial Sovereignty: In countries with unstable currencies or restrictive financial systems, Bitcoin provides individuals with a way to protect and access their wealth.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its advantages, Bitcoin faces challenges. Its price volatility can deter mainstream adoption, as sudden fluctuations make it difficult to use as a stable medium of exchange. Scalability is another issue; the network can only process a limited number of transactions per second. Additionally, Bitcoin’s energy-intensive mining process has sparked environmental concerns, prompting calls for more sustainable solutions.
Exploring the World of Bitcoin
Bitcoin represents a paradigm shift in how we think about money, offering an alternative to traditional financial systems that is decentralized, transparent, and accessible. Its potential to empower individuals, foster financial inclusion, and drive innovation makes it a significant player in the global economy.
For beginners, Bitcoin’s complexity can be intimidating, but understanding its history, purpose, and mechanics reveals a technology with transformative potential. Whether you’re looking to invest, use Bitcoin for payments, or explore its role in reshaping finance, now is the time to dive deeper into this revolutionary digital currency.















No Responses