Blockchains do not run on slogans or price charts. They run on ordered events. Every transaction, audit log, settlement window, and compliance record depends on time being consistent across systems that never share a single clock. When timestamps drift, records fracture. Trust erodes quietly. Accurate time is not a feature, it is shared infrastructure that […]
Find Guidance On Recovering Access To A Lost Bitcoin Wallet Bitcoin ownership is tied directly to access. Unlike banks or credit cards, there’s no customer service hotline or reset button when something goes wrong. If someone loses access to their wallet, their funds may become permanently unreachable. That’s why wallet access matters so much. Whether […]
Learn How Hardware Wallets Protect Your Bitcoin From Online Threats Bitcoin ownership is tied to a private key—a secret code that allows you to spend your coins. If someone gets hold of your private key, they can move your funds. That’s why protecting it is the most important part of using Bitcoin securely. Many users […]
Why Privacy Matters for Bitcoin Users Bitcoin is often called private, but the reality is more complex. Every transaction is recorded on a public ledger. While addresses don’t show personal names, they can still be linked to identities through repeated use or poor security habits. This means that if someone tracks your online activity, they […]
Understand How Bitcoin Manages Trust, Security, And Currency Flow Traditional currencies rely on central banks to issue money, control interest rates, and manage inflation. In contrast, Bitcoin eliminates the need for a central institution. Instead, the system operates through software and shared rules, removing government control entirely. This difference creates significant implications for users. Bitcoin’s […]
Why Bitcoin Needs Help Processing More Transactions Bitcoin was designed to be secure and decentralized, not fast. Each block is mined roughly every 10 minutes, and the network can only handle around seven transactions per second. That limit causes delays and higher fees when demand rises sharply. This bottleneck has real effects. During busy periods, […]
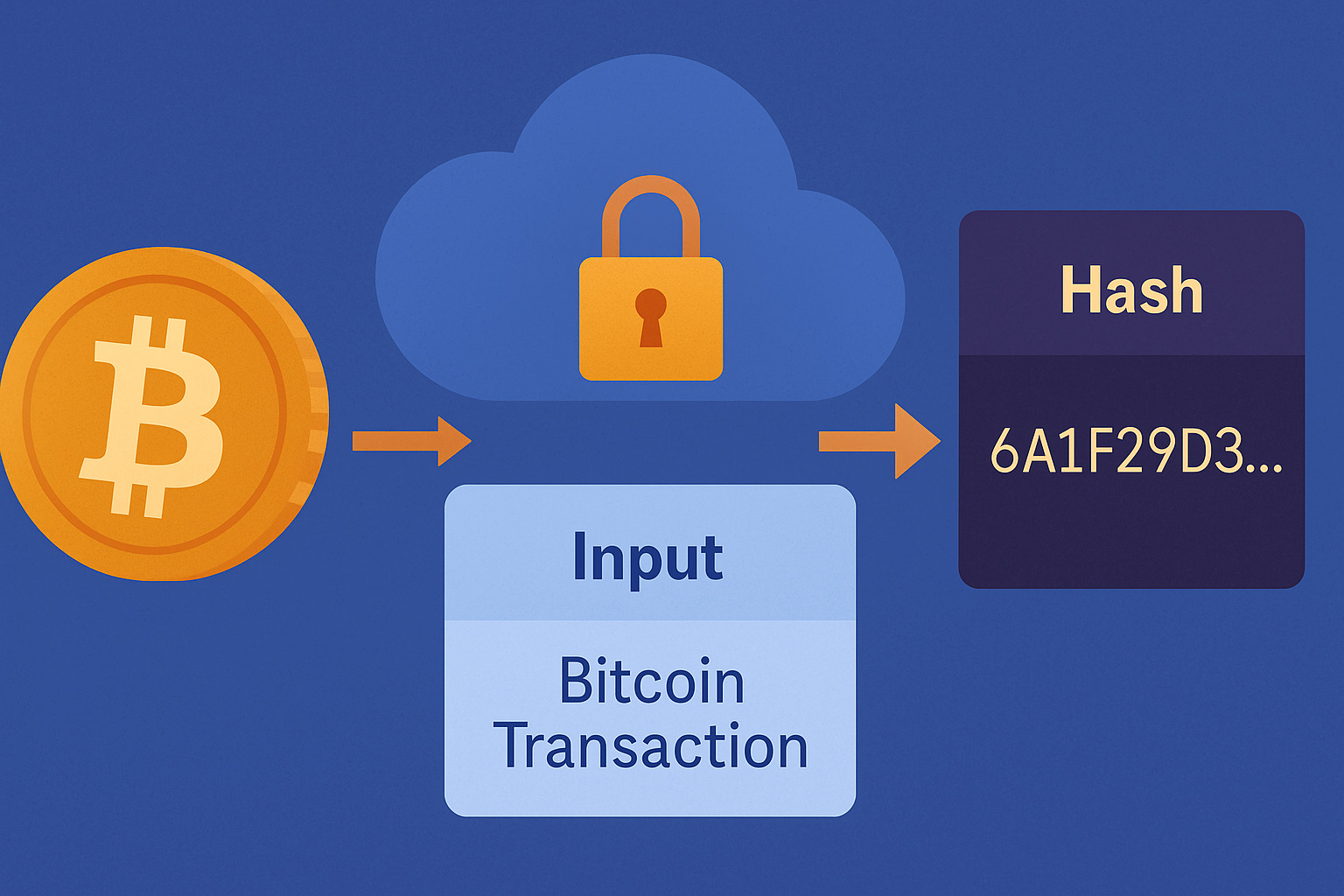
Understand How Hash Functions Keep Bitcoin Transactions Safe When people talk about Bitcoin’s security, the term “hash function” often comes up. It might sound technical, but it plays a vital role in how transactions stay trustworthy. Every time someone sends or receives Bitcoin, a hash function helps verify the action behind the scenes. A hash […]
Precautions Taken by Bitcoin Traders in Digital Transactions Using Bitcoin has become common among people seeking an alternative way to handle money online. However, as cryptocurrency adoption increases, so do online threats. From phishing emails to data leaks, traders face significant risks if they aren’t cautious. One simple precaution many traders take is using a […]
Why Bitcoin Halving Events Are Watched Closely Bitcoin halving isn’t a random event—it’s one of the most anticipated moments in the cryptocurrency timeline. It happens roughly every four years and directly cuts the reward that miners receive for validating transactions. The impact stretches far beyond mining alone. The reason it matters is simple: fewer rewards […]
Explore The True Expenses Behind Bitcoin Mining Bitcoin mining started as a niche activity done on home computers. Now, it’s a full-scale industry drawing attention from investors, tech entrepreneurs, and even governments. The chance to earn bitcoin by helping secure the network seems appealing. But behind that promise lies a complex balance of cost and […]