Why Bitcoin Needs Help Processing More Transactions Bitcoin was designed to be secure and decentralized, not fast. Each block is mined roughly every 10 minutes, and the network can only handle around seven transactions per second. That limit causes delays and higher fees when demand rises sharply. This bottleneck has real effects. During busy periods, […]
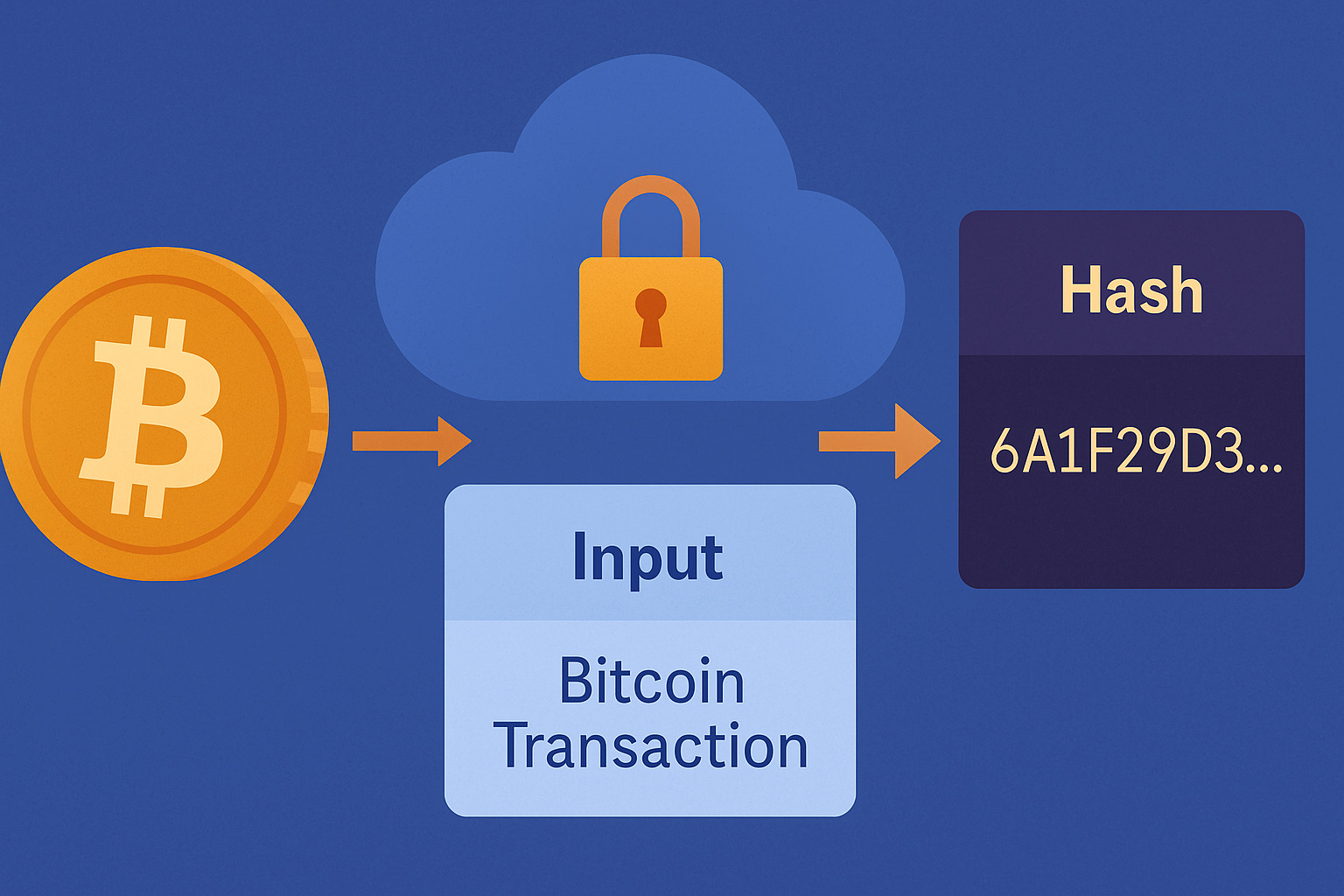
Understand How Hash Functions Keep Bitcoin Transactions Safe When people talk about Bitcoin’s security, the term “hash function” often comes up. It might sound technical, but it plays a vital role in how transactions stay trustworthy. Every time someone sends or receives Bitcoin, a hash function helps verify the action behind the scenes. A hash […]
Understanding the Basics of Ordinals on Bitcoin Ordinals bring a new layer of meaning to Bitcoin by assigning unique identities to individual satoshis—the smallest unit of BTC. Through a method called “inscription,” each satoshi can now carry data, such as images, text, or code. This process has turned Bitcoin into more than just a currency; […]
Why understanding Bitcoin software options matters Bitcoin is more than just a digital currency. It’s a network powered by different types of software, each with its own purpose. One of the most talked-about is Bitcoin Core—a reference point in the ecosystem. But it’s not the only option available. Understanding how it compares to other software […]
Understanding the Importance of Running Your Own Node Every transaction that takes place on the Bitcoin network relies on users who help ensure its integrity and accuracy. One of the most meaningful ways to participate is by running a full node. Having your own node provides not only control, but also a deeper connection to […]
Accelerating Transactions with Layer-Two Technology In Bitcoin’s early years, transaction speed became a major issue—especially during times of high traffic. Due to blockchain’s design, the number of transactions per block is limited. As demand rises, so do fees and waiting times. This is where the concept of the Lightning Network emerged as a solution. The […]
Understanding Bitcoin’s UTXO Model: How Transactions Work Bitcoin continues to gain traction worldwide, with more people using it in various ways. As adoption grows, many are curious about how its transaction system actually works. Unlike traditional banking, which has a clear account balance structure, Bitcoin operates on a unique model called the Unspent Transaction Output […]
The Primary Role of Bitcoin Nodes Bitcoin is one of the most influential technological inventions of our time. It is not just a digital currency but a decentralized system that operates without a central authority. One of the most crucial aspects of Bitcoin is how it ensures transaction security and the integrity of the blockchain. […]
Bitcoin and Smart Contracts: What’s the Connection? Bitcoin has long been recognized as a digital currency, but it was not originally designed for smart contracts like Ethereum. However, over time, improvements have been made to enhance its ability to support more sophisticated transactions. The introduction of the Taproot upgrade is a significant step in making […]
The Importance of Data Organization in Bitcoin Trading Bitcoin trading relies on real-time data streams from multiple sources, including cryptocurrency exchanges, market order books, and blockchain transactions. Unlike traditional financial markets, Bitcoin operates 24/7, generating vast amounts of trading data that must be analyzed quickly to make informed decisions. Without proper data organization, traders risk […]