Find Guidance On Recovering Access To A Lost Bitcoin Wallet Bitcoin ownership is tied directly to access. Unlike banks or credit cards, there’s no customer service hotline or reset button when something goes wrong. If someone loses access to their wallet, their funds may become permanently unreachable. That’s why wallet access matters so much. Whether […]
Learn How Hardware Wallets Protect Your Bitcoin From Online Threats Bitcoin ownership is tied to a private key—a secret code that allows you to spend your coins. If someone gets hold of your private key, they can move your funds. That’s why protecting it is the most important part of using Bitcoin securely. Many users […]
Why Privacy Matters for Bitcoin Users Bitcoin is often called private, but the reality is more complex. Every transaction is recorded on a public ledger. While addresses don’t show personal names, they can still be linked to identities through repeated use or poor security habits. This means that if someone tracks your online activity, they […]
Precautions Taken by Bitcoin Traders in Digital Transactions Using Bitcoin has become common among people seeking an alternative way to handle money online. However, as cryptocurrency adoption increases, so do online threats. From phishing emails to data leaks, traders face significant risks if they aren’t cautious. One simple precaution many traders take is using a […]
Understanding Why Password Strength Matters Bitcoin wallets are secured by private keys and passwords that act as digital locks. If someone gains access to them, your funds could vanish in seconds. That’s why strong password habits are not just recommended—they’re a core part of protecting your assets. A common mistake is relying on passwords that […]
Why a Recovery Phrase Deserves Serious Attention A recovery phrase is the master key to your bitcoin wallet. If lost, stolen, or exposed, it can mean permanent loss of access to your funds. Unlike traditional banking, there’s no customer support to call for password resets. The responsibility—and the risk—rests entirely with the holder. Because of […]
Understanding the Importance of Offline Protection Holding bitcoin isn’t just about making a profit—it also comes with the responsibility of keeping it secure. Every day, new threats emerge from hackers trying to steal private information. Because of this, many users turn to what’s known as cold storage. Cold storage is a method of storing cryptocurrency […]
Why It’s Important to Tell the Real from the Fake More and more people are entering the world of cryptocurrency. Reasons include the potential for profit, the decentralized nature of the system, and the ease of accessing digital transactions. However, as interest grows, so do the number of deceptive platforms. One of the most dangerous […]
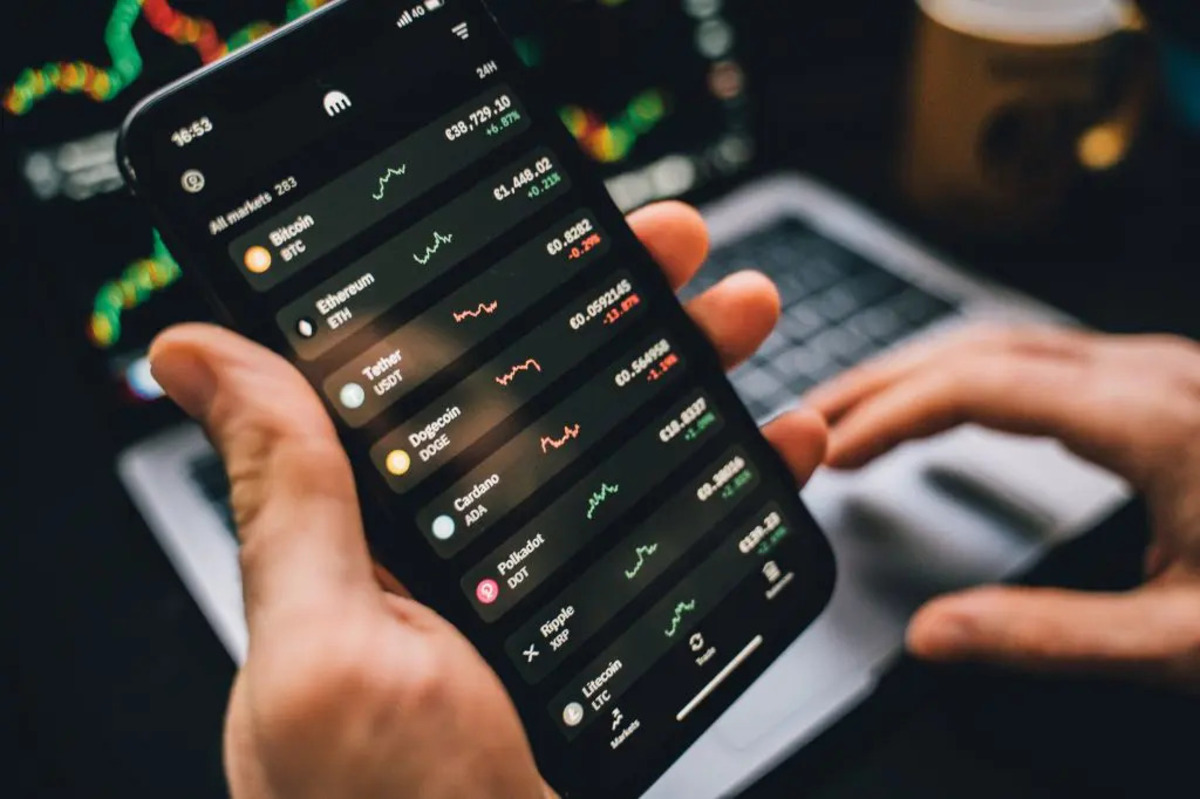
Focusing on time is key to navigating the market effectively Unlike the stock market, which opens and closes at specific hours, the Bitcoin market operates 24/7—including weekends and holidays. However, while the market is always active, price movements tend to be stronger during certain hours depending on the time zones of active traders. When major […]
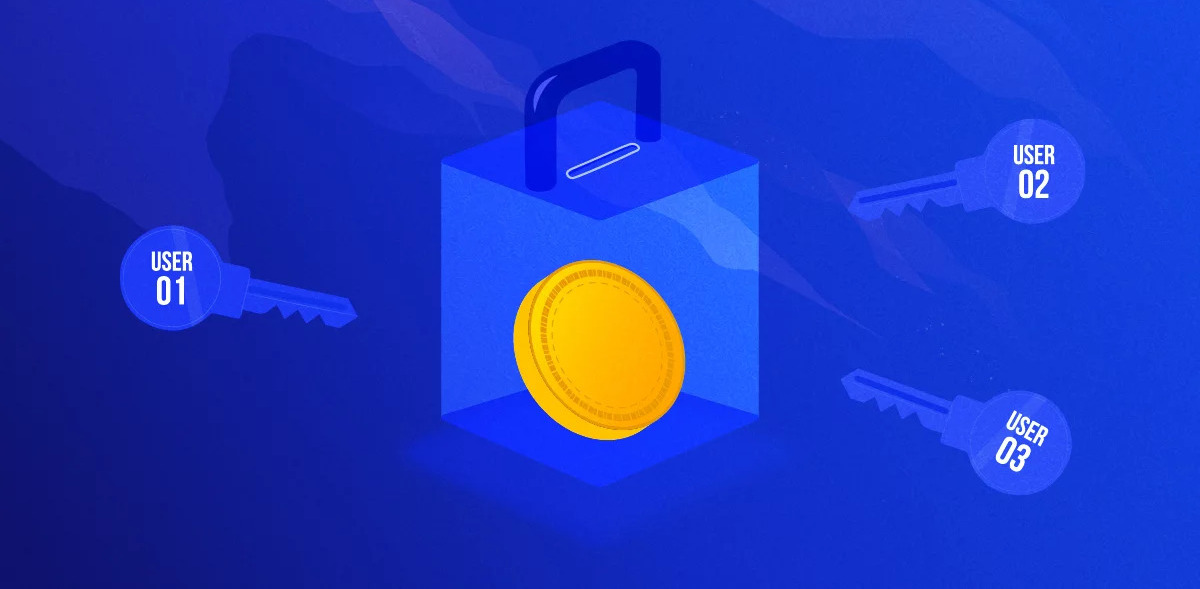
Protecting digital assets through shared control and reduced risk In the world of Bitcoin, a single wallet can hold significant value. If only one person has access, the risk of loss becomes high—whether due to hacking or accidental key loss. A single misstep can lead to irreversible damage. Multi-signature wallets, or “multisig” wallets, offer a […]